To decrease the incidence of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression in patients when administered prior to a platinum/etoposide-containing regimen or topotecan-containing regimen
For extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC)
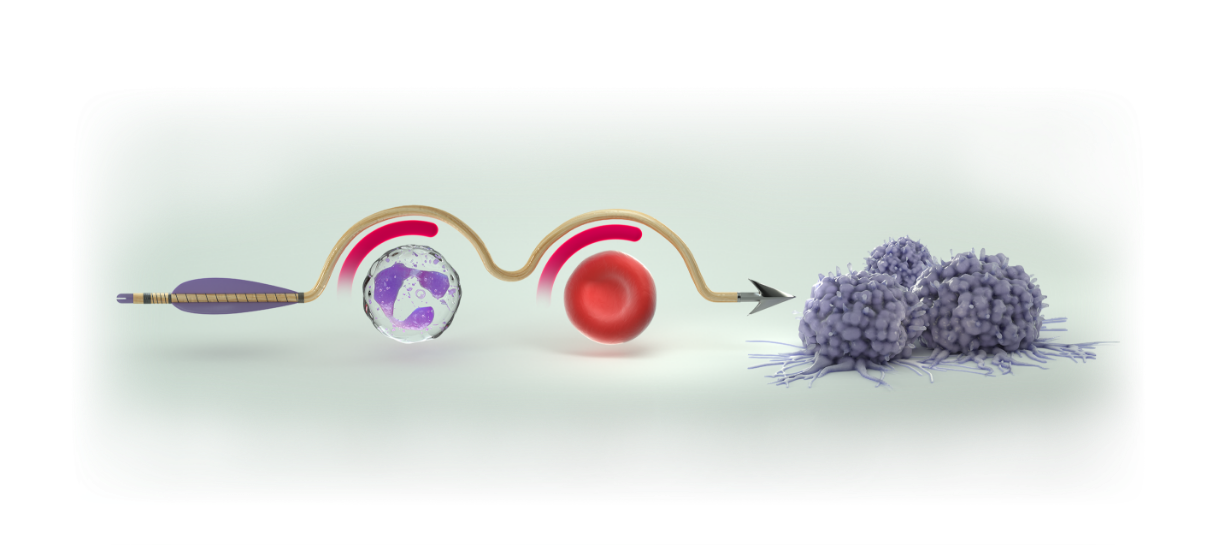
SPARE THE MARROW. SPEAR THE TUMOR.
COSELA HELPS PROTECT AGAINST myelosuppression, while chemotherapy targets cancer cells
COSELA® (trilaciclib) helps protect hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs), the source of blood cell lineages, including neutrophils, red blood cells, and platelets

The First and Only Proactive Multilineage Myeloprotection Therapy

|
In the Pivotal Study in 1st-Line ES-SCLC, COSELA administered before an etoposide/carboplatin + atezolizumab (E/P/A) regimen resulted in1: |
|
|---|---|
 |
REDUCED INCIDENCE AND DURATION OF SEVERE NEUTROPENIAPrimary Endpoints: 1.9% vs 49.1% (P<0.0001) and 0 days vs 4 days (P<0.0001) with and without COSELA, respectively* |
 |
NUMERICALLY LOWERED INCIDENCE OF GRADE 3/4 ANEMIA AND RBC TRANSFUSIONSSecondary Endpoints: 19% vs 28% and 13% vs 21% with and without COSELA, respectively† |
 |
REDUCED INCIDENCE OF GRADE 3/4 THROMBOCYTOPENIASecondary Endpoint: 1.9% vs 37.7% with and without COSELA (P=0.0026)‡ |
 |
REDUCED RATE OF CHEMOTHERAPY DOSE REDUCTIONSSecondary Endpoint: 2.1 vs 8.5 with and without COSELA (P=0.0195)§ |
| * | Multiplicity-adjusted P values. Adjusted relative risk (aRR) 0.038 (95% CI, 0.008, 0.195) and mean difference -3.6 (95% CI, -4.9, -2.3), respectively. Duration evaluated in Cycle 1. |
| † | aRR 0.663 (95% CI, 0.336, 1.310) and aRR 0.642 (95% CI, 0.294, 1.404). Red blood cell (RBC) transfusions measured on/after 5 weeks. Grade 3/4 anemia defined as Grade 3/4 decreased hemoglobin. |
| ‡ | Raw one-sided P value not adjusted for multiplicity. aRR 0.053 (95% CI, 0.008, 0.356). Platelet endpoint results were not consistent across studies. See Study 2. See Study 3. |
| § | Raw one-sided P value not adjusted for multiplicity. Rate of all-cause dose reductions, events per 100 cycles. aRR 0.242 (95% CI, 0.079, 0.742). |
Standard-of-care supportive interventions, including RBC and platelet transfusions, were allowed per investigator discretion throughout the entire treatment period. Primary prophylaxis with granulocyte colony-stimulating factors (G-CSFs) and use of erythropoiesis stimulating agents (ESAs) were prohibited in Cycle 1 of induction, although therapeutic G-CSF was allowed in all cycles. More patients in the E/P/A regimen arm without COSELA received G-CSF Administration (47.2% vs 29.6%, aRR 0.646 [95% CI, 0.403, 1.034]) and had ESA use (11% vs 6%, aRR 0.529 [95% CI, 0.145, 1.927]) vs with COSELA, respectively.
COSELA: A STANDARD OF CARE



IMPROVING MY ES-SCLC PATIENTS’ EXPERIENCE
NARRATOR (00:09)
COSELA is indicated to decrease the incidence of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression in adult patients when administered prior to a platinum/etoposide-containing regimen or topotecan-containing regimen for ES-SCLC.
Jason Porter, MD
So extensive-stage small cell lung cancer is a really dismal disease and those patients usually have a very poor prognosis.
And so, my goal is for the patient experience, as well as the family experience, to be better, for those patients to live as long as possible, to be as healthy as possible, and to enjoy their time.
For me, COSELA is now a standard of care. When I look at the data, I can't imagine not giving my patients the opportunity that COSELA affords, for them to stay on therapy, at the prescribed doses, and to stay on schedule. I feel like that's the fair thing to do for my patient, and so, for me, it's a standard.
Most patients are excited about it when I tell them the benefits of using COSELA, especially when they hear that it'll decrease their need for transfusions or delays in their therapy.
As far as keeping our chemotherapy treatments on course, I've done a look back at my patients since I've started using COSELA. And I see less dose reduction and I see less rescheduling, for those patients.
So, it's my experience that I'm, I'm seeing less cytopenia and I'm having less transfusions since starting COSELA for my small cell patients.
NARRATOR
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
COSELA is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity reactions to trilaciclib.
Warnings and precautions include injection-site reactions (including phlebitis and thrombophlebitis), acute drug hypersensitivity reactions, interstitial lung disease (pneumonitis), and embryo-fetal toxicity.
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) were fatigue, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, aspartate aminotransferase increased, headache, and pneumonia.
This information is not comprehensive. Please see the full Prescribing Information at COSELA.com


IMPROVING MY ES-SCLC PATIENTS’ EXPERIENCE
NARRATOR (00:09)
COSELA is indicated to decrease the incidence of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression in adult patients when administered prior to a platinum/etoposide-containing regimen or topotecan-containing regimen for ES-SCLC.
Jason Porter, MD
So extensive-stage small cell lung cancer is a really dismal disease and those patients usually have a very poor prognosis.
And so, my goal is for the patient experience, as well as the family experience, to be better, for those patients to live as long as possible, to be as healthy as possible, and to enjoy their time.
For me, COSELA is now a standard of care. When I look at the data, I can't imagine not giving my patients the opportunity that COSELA affords, for them to stay on therapy, at the prescribed doses, and to stay on schedule. I feel like that's the fair thing to do for my patient, and so, for me, it's a standard.
Most patients are excited about it when I tell them the benefits of using COSELA, especially when they hear that it'll decrease their need for transfusions or delays in their therapy.
As far as keeping our chemotherapy treatments on course, I've done a look back at my patients since I've started using COSELA. And I see less dose reduction and I see less rescheduling, for those patients.
So, it's my experience that I'm, I'm seeing less cytopenia and I'm having less transfusions since starting COSELA for my small cell patients.
NARRATOR
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
COSELA is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity reactions to trilaciclib.
Warnings and precautions include injection-site reactions (including phlebitis and thrombophlebitis), acute drug hypersensitivity reactions, interstitial lung disease (pneumonitis), and embryo-fetal toxicity.
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) were fatigue, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, aspartate aminotransferase increased, headache, and pneumonia.
This information is not comprehensive. Please see the full Prescribing Information at COSELA.com

INTEGRATED SAFETY ACROSS STUDIES
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) were fatigue, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, aspartate aminotransferase increased, headache, and pneumonia.
See Safety Data >Trilaciclib (COSELA) is a recommended option by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)ΙΙ¶
INDICATION: Trilaciclib (COSELA) is indicated to decrease the incidence of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression in adult patients when administered prior to a platinum/etoposide-containing regimen or topotecan-containing regimen for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).
ΙΙReferenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Small Cell Lung Cancer V.3.2023. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2023. All rights reserved. Accessed January 27, 2023. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org.
¶Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Hematopoietic Growth Factors V.1.2023. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2023. All rights reserved. Accessed January 27, 2023. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org.
NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use, or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®).
THE FIRST & ONLY MYELOPROTECTION THERAPY
COSELA helps protect hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs), the source of multiple blood cell lineages, including neutrophils, red blood cells, and platelets. Watch the COSELA mechanism of action (MOA) video to learn about the proactive and multilineage MOA.
Additionally, find key insights from a leading medical oncologist.
Explore the MOA >REVIEW PATIENT-REPORTED OUTCOMES DATA
QUICK LINKS
RESOURCES FOR Healthcare Professionals